
Look for other features of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy if the preceding J-point is not elevated. These ECG changes, including T-wave inversions, can often return to normal with detraining (see below ECGs) outside the context of age <16 years and black ethnicity, T wave inversions beyond V2 should be investigated.
Sinus bradycardia <40 bpm, Mobitz type 1 second degree AVB and junctional rhythm are not uncommon and don't warrant further investigation in asymptomatic athletes. Isolated Sokolow-Lyon voltage criterion for LVH is common in male athletes and does not warrant further investigation.Increased vagal tone (e.g., sinus bradycardia, first degree atrioventricular block ) and increased chamber size due to physiologic remodeling (e.g., left ventricular hypertrophy, bi-atrial enlargement) account for normal ECG patterns seen in highly trained athletes.The following are key points from his talk: Sanjay Sharma, co-senior author of the International Recommendations for ECG Interpretation in Athletes, reviewed his approach to the Athlete's ECG. We hope you enjoy the summaries.Įditorial Team Lead, Sports & Exercise Cardiology Clinical Topic Collectionĭr. Thank you to the FITs for all their hard work.
#PATHOLOGICAL Q WAVE DRIVER#
Please feel free to contact Chris Driver ( or me ( with any questions.
#PATHOLOGICAL Q WAVE FULL#
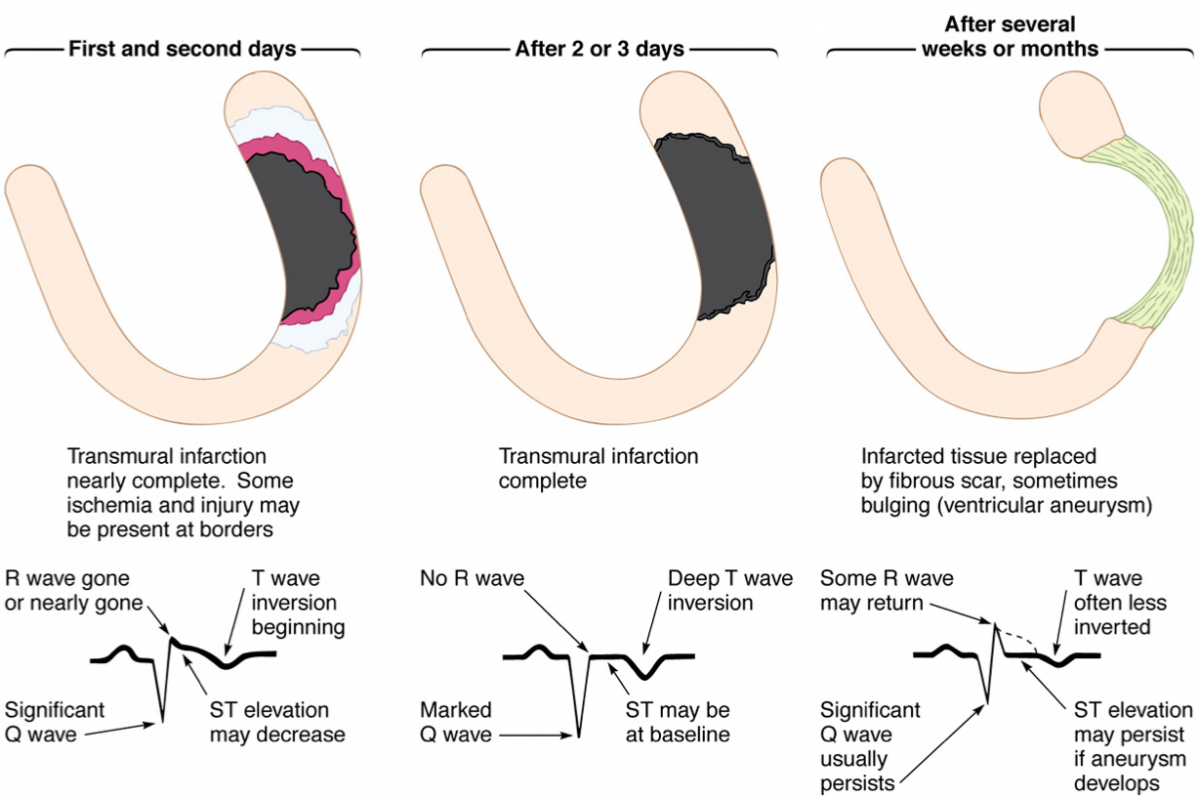
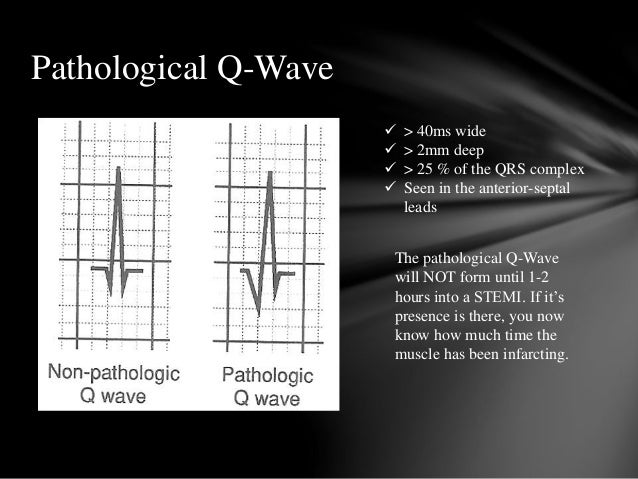
The full CAH agenda can be accessed here. Most of them were presenters at CAH, and all are active in the Sports and Exercise Cardiology Section FIT Interest Group. In the next few weeks, we will post summaries of key sessions written by cardiology Fellows-in-Training (FIT). The overflow capacity of attendees and number of live streaming participants exceeded 220 in total. As a result, if MI is suspected, a doctor must check the ECG of the patient to see if there are any abnormalities that could indicate heart problems.Dear Sports and Exercise Cardiology Enthusiasts:Ĭare of the Athletic Heart 2019 (CAH), directed by Matthew Martinez MD, and Jonathan Kim, MD, convened June 20-22 at the American College of Cardiology's Heart House in Washington, DC. Abnormal Q waves on admission ECG of patients with inferior MI have no negative effect on their survival prospects. Because the scar tissue in a myocardial infarction is electrically dead, pathologic Q waves are produced, which is a elecrical ‘hole.’ According to research, abnormal Q waves on the admission electrocardiogram (ECG) are linked to creatine kinase levels in the blood, heart failure prevalence, and mortality in patients with anterior MI. They occur due to an absence of electrical current. If you have had a previous myocardial infarction, you should be able to detect pathological Q waves. Pathologic Q Waves And Risk Of Mortality In Patients With Myocardial Infarction The q waves represent abnormal electrical activity in the heart and can be used to diagnose a heart attack. Pathologic q waves on an electrocardiogram (ECG) are usually caused by myocardial infarction (heart attack). If you suspect that Q waves have formed on your ECG, you should consult with a doctor. A Q wave can also be seen in other heart conditions such as subacute myocardial infarction, myocardial infarction, or accessory pathway infarction.

Q waves are characterized by a 12 hour period of development, and they may not appear in all patients with AMI. When pathological Q waves are present, an infarct does not always occur. When Q waves first appear, they can be linked to acute myocardial infarction (AMI). The amplitude (measured in millimeters) for infants is higher than 14 mm (7 for most). In pediatric patients, Q waves can be seen on the inferior and left lateral leads of the peripheral arteries and are typically observed within 20 minutes. In the case of Q waves on an ECG, you should consult with a doctor to figure out what is causing it. Why Q Waves On An Ecg Aren’t Always An Indicator Of A Heart ProblemĪn electrocardiogram (ECG) may not always reveal any obvious sign of a heart problem. A variety of noninfarct settings can also detect prominent Q waves, though these are more common in patients who have myocardial infarctions. In theory, Q waves indicate the net direction of early ventricular depolarization (QRS) electrical forces towards the negative pole of the lead axis at the center of the waves.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
